
Regulation of bulge cell activities involves many signaling pathways, such as Wnt/β-catenin, BMP/Smad, and Sonic hedgehog (Shh) signaling. It is a convex protrusion of outer root sheath in the most distal permanent portion of hair follicle, just below the sebaceous gland. The regenerative capacity of hair follicles depends on a group of keratinocyte and melanocyte steam cells that are located in the follicular bulge area. This cyclic transformation is controlled by finely tuned changes in the local signaling milieu, based on changes in the expression of cytokines, hormones, neurotransmitters as well as transcription factors and enzymes. Traditionally, three phases of hair growth were recognized, including anagen, with classification ranging from stages I to VI (a period of very rapid growth, pigmentation, and hair-shaft production), catagen (regression phase), and telogen (resting phase). Hair follicles undergo lifelong, cyclic transformation. In addition, no specific target autoantigen has been identified so far, and autoantibodies to hair follicle-associated antigens are detectable in normal individuals. High frequency of a positive family history up to 42% may reflects the contribution of heredity factors. Some investigators believed that alopecia areata is not a truly autoimmune disease but is only ‘consistent with’ autoimmune mechanisms. It suggests involvement of melanogenesis-associated autoantigens as a target epitope. Antibodies against multiple components of hair follicles almost exclusively attack in anagen phase, where melanogenesis takes place. Higher incidence rate in the female population and increased overall risk of other autoimmune disorders militate in favor of autoimmune hypothesis. Despite its high incidence, the pathobiology is not fully understood, and no single concept could be universally accepted.Īlopecia areata is mostly considered to be an autoimmune disease, in which the collapse of hair follicle immune privilege plays a key role. In both cases, the effectiveness of these treatment types can vary depending on the person and may be long term to ensure hair continues to grow.Alopecia areata is a condition that affects hair follicles and leads to hair loss ranging from small well-defined patches to complete loss of all body hair. The difference is, treatments for AT are focused on regrowing the hair lost on the scalp, whereas treating AU requires targeting hair follicles on the entire body.

Now you are familiar with some of the treatment options for AU, how about Alopecia Totalis? This subtype is also treated using the same treatment types listed above. Whether a specific treatment is suitable for a child is left to the discretion of the dermatologist, and the comfort level of the parents and child. JAK inhibitors (baricitinib, tofacitinib, ruxolitinib)įor children, treatment options are less extensive.immunosuppressive medications (methotrexate, cyclosporine).corticosteroids (topical steroids, steroid injections, prednisone, clobetasol).
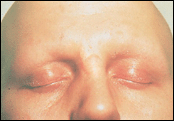
topical immunotherapy such as diphencyprone (DPCP) or squaric acid (SADBE).For adults with AU, common treatment options include:
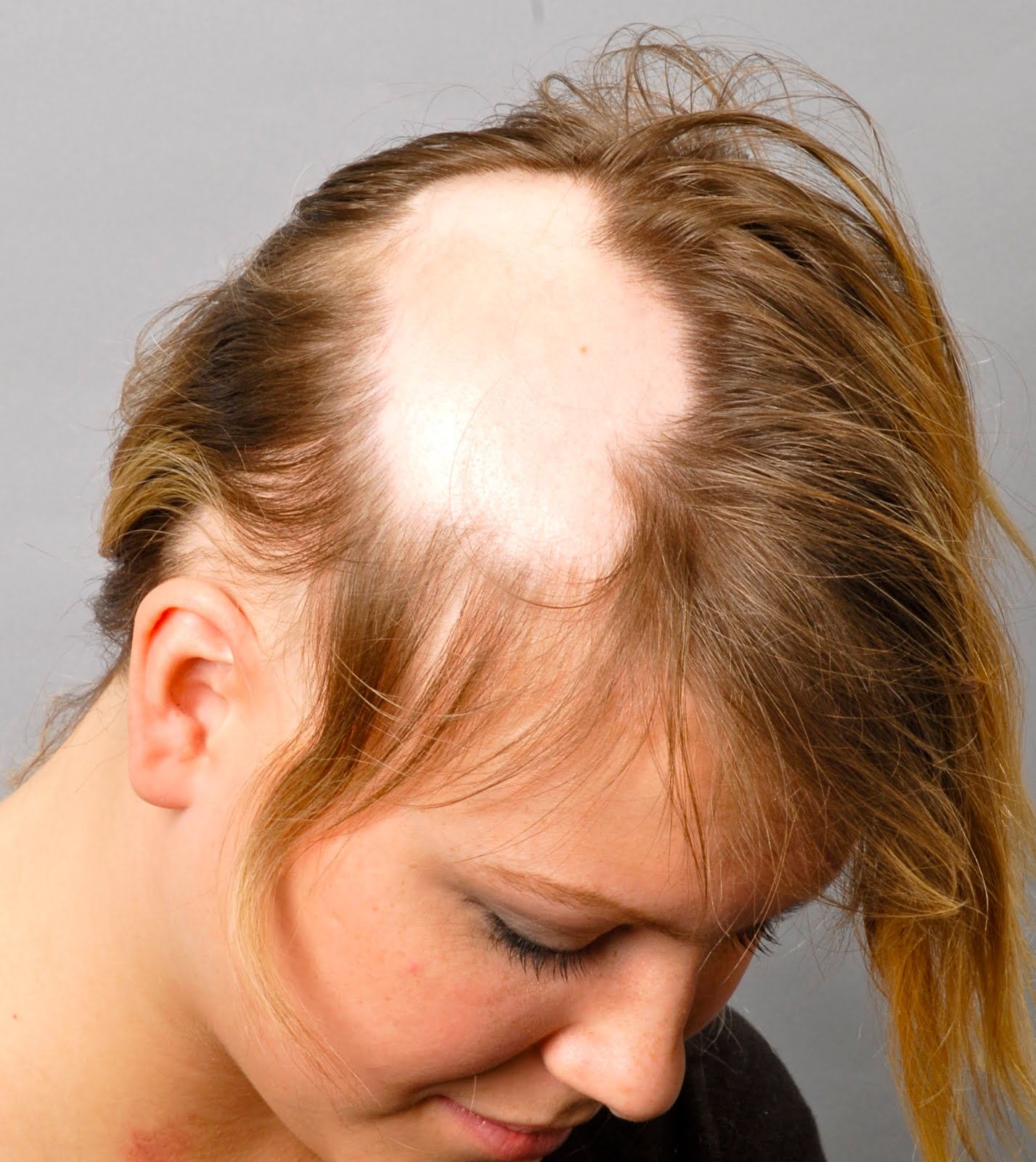
What course of treatment your dermatologist recommends will be dependent on what subtype of Alopecia Areata you have. There is currently no cure for Alopecia Areata but there are a variety of treatment options.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
